If you’re new to the United States, building credit can feel confusing, frustrating, and even unfair. You may have had a strong financial history in your home country — paid loans on time, owned property, used credit responsibly — yet in the US you start from zero.
No credit history.
No credit score.
No track record.
The reality is simple: in America, your credit score controls access to financial opportunity. Without it, you may struggle to:
- Rent an apartment
- Finance or lease a car
- Qualify for a regular credit card
- Get lower insurance rates
- Secure better loan terms
The good news? You can build credit safely, legally, and predictably — if you follow the right steps.
This guide explains exactly how to build credit in the US step by step — especially if you’re a beginner or an immigrant starting from scratch.
What Is a Credit Score in the US?
A credit score is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness. In simple terms, it tells lenders how risky it is to lend you money.
The most commonly used scoring model is FICO, which ranges from 300 to 850.
Here’s a general breakdown:
- 300–579 → Poor
- 580–669 → Fair
- 670–739 → Good
- 740–799 → Very Good
- 800–850 → Exceptional
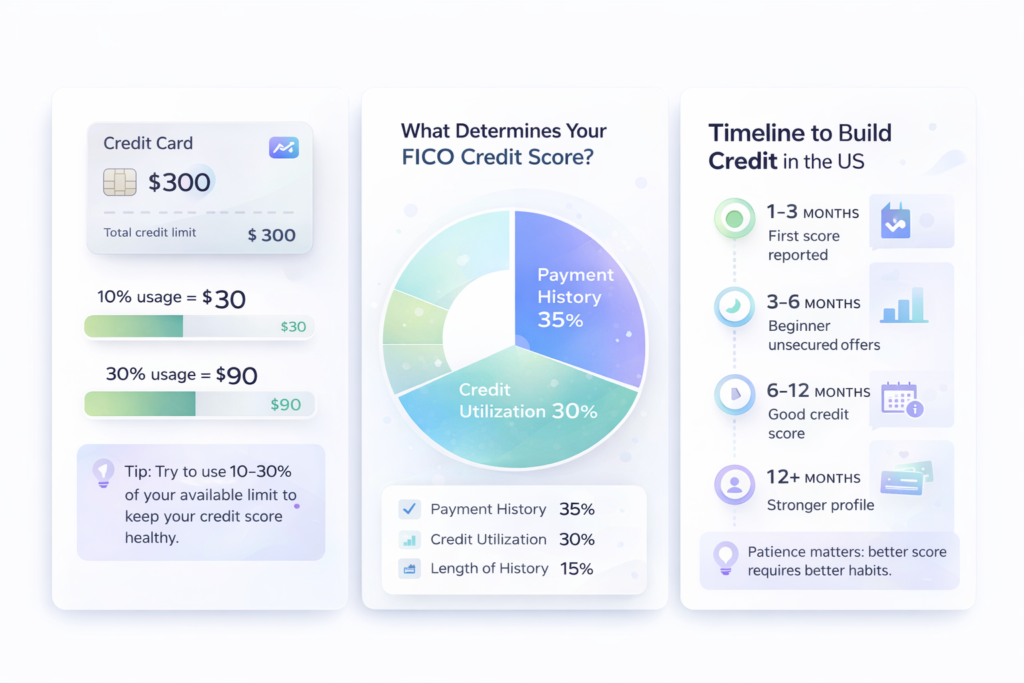
Your credit score is calculated based on five major factors:
- Payment history (35%) – Do you pay on time?
- Credit utilization (30%) – How much of your limit are you using?
- Length of credit history (15%) – How long have accounts been open?
- Credit mix (10%) – Different types of credit (cards, loans)
- New credit inquiries (10%) – How often you apply
If you’re new to the US, you usually start with no score at all — which is different from bad credit.
Why Newcomers Start With No Credit
One of the most confusing things for immigrants is this:
The US does not import foreign credit history.
Even if you had perfect credit in Europe, Asia, or Latin America, it does not automatically transfer to American credit bureaus.
That means:
- You are not “bad credit”
- You are not “rejected”
- You simply have no US credit file yet
And without data, the system cannot calculate a score.
The goal is to create that first positive data point.
Step 1: Get an SSN or ITIN
Before you can build credit, you need a way to be identified in the system.
Option 1: Social Security Number (SSN)
If you have work authorization in the US, you likely have or can obtain an SSN. This is the simplest path.
Option 2: Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
If you don’t qualify for an SSN, you may apply for an ITIN through the IRS. Some banks and credit card issuers accept ITIN applicants.
Important: Not all lenders accept ITIN, so you must verify before applying.
Without SSN or ITIN, most major credit-building options are not available.
Step 2: Open a Secured Credit Card
For most beginners and immigrants, a secured credit card is the safest and fastest way to build credit in the US.
What Is a Secured Credit Card?
A secured card requires a refundable security deposit.
Example:
- You deposit $300
- Your credit limit becomes $300
You are essentially borrowing against your own deposit.
Because the bank has collateral, approval rates are much higher for people with no credit history.
Why Secured Cards Work
They report your activity to credit bureaus just like regular credit cards. If you use it correctly:
- You build payment history
- You establish utilization behavior
- You create your first credit record
That’s exactly what you need.
Step 3: Use Less Than 30% of Your Limit (Ideally Under 10%)
Credit utilization is one of the biggest factors in your score.
If your credit limit is $300:
- 30% = $90
- 10% = $30
Try to keep your balance below $30–$60.
Many beginners make this mistake:
They think using the full limit helps build credit faster.
It does not.
High balances hurt your score — even if you pay on time.
Lower usage signals financial discipline.
Step 4: Always Pay On Time — No Exceptions
Payment history makes up 35% of your credit score.
One missed payment can significantly damage a young credit file.
To avoid this:
- Turn on autopay
- Set it to pay the full statement balance
- Never carry unnecessary interest
Important distinction:
There is no need to carry a balance or pay interest to build credit.
Paying in full every month builds credit just as effectively — without costing you money.
Step 5: Let the Account Age (Patience Matters)
After opening your first secured card:
- Do not apply for multiple cards immediately
- Avoid unnecessary hard inquiries
- Let the account age for 3–6 months
Time is a critical factor.
Your credit profile becomes stronger as it ages.
Many beginners damage their progress by applying too aggressively.
Slow growth is strong growth.
How Long Does It Take to Build Credit in the US?
Here is a realistic timeline:
1–3 Months
Your score may appear after at least one reporting cycle.
3–6 Months
You may qualify for beginner unsecured cards.
6–12 Months
You can build into the “good” range (670+).
12+ Months
Your profile becomes stable and more attractive to lenders.
Building credit is not instant — but it is predictable if done correctly.
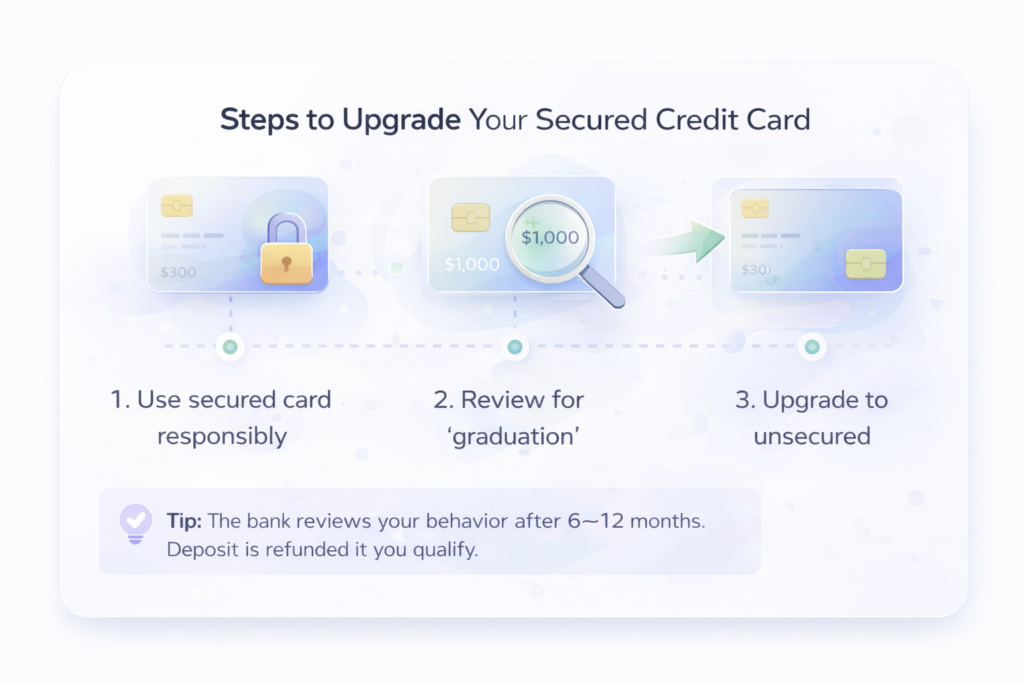
When Can You Get an Unsecured Credit Card?
After 6–12 months of responsible use:
- On-time payments
- Low utilization
- No missed payments
You may qualify for a regular (unsecured) credit card.
Many secured cards automatically review your account for graduation. If approved:
- Your deposit is refunded
- Your limit may increase
- Your credit history continues uninterrupted
This is the ideal progression.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are the most common errors beginners make when building credit in the US:
1. Maxing Out the Card
Using 90–100% of your limit signals risk.
2. Missing a Payment
Even one 30-day late mark can stay on your report for years.
3. Applying for Too Many Cards
Multiple hard inquiries reduce your score and look desperate.
4. Closing Your First Card Too Early
Length of history matters. Your first card is valuable.
5. Falling for “Credit Repair” Scams
No company can magically fix credit legally. Avoid services promising instant 750+ scores.
You build credit through behavior, not shortcuts.

Can Immigrants Build Credit Without an SSN?
In some cases, yes — through ITIN-based cards.
However:
- Options are more limited
- Approval criteria may vary
- Research is required
If possible, obtaining an SSN simplifies the process significantly.
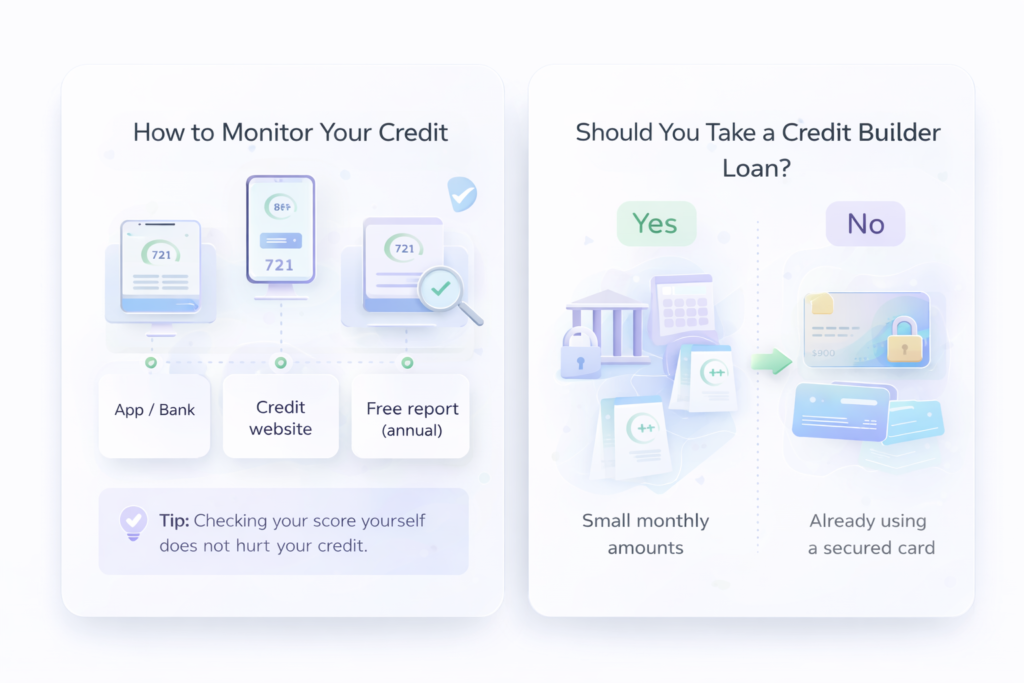
Should You Take Out a Credit Builder Loan?
Some banks and credit unions offer “credit builder loans.”
These are small installment loans designed to help create payment history.
They can be useful — but they are not necessary if:
- You are already using a secured credit card responsibly
- You prefer not to add complexity
For beginners, simplicity is often better.
What Is a Good Credit Score for Beginners?
After your first year, a realistic target is:
670+ (Good)
At this point, you may qualify for:
- Better credit cards
- Lower auto loan rates
- Stronger rental applications
Reaching 700+ within 12–18 months is achievable with disciplined behavior.
How to Build Credit Faster (Safely)
If you want to accelerate progress:
- Keep utilization under 10%
- Ask for credit limit increases (after 6+ months)
- Become an authorized user on a well-managed account
- Keep accounts open long-term
Never rush the process through risky borrowing.
Consistency beats speed.
Does Checking Your Credit Score Hurt It?
No — checking your own credit score does not lower it.
This is called a “soft inquiry.”
However, applying for credit results in a “hard inquiry,” which can slightly reduce your score temporarily.
Monitoring your credit is smart and responsible.
Final Advice: Build Slowly, Build Safely
Building credit in the US is not about gaming the system.
It is about proving reliability over time.
If you:
- Use a secured card
- Keep utilization low
- Pay in full and on time
- Avoid unnecessary applications
You will build strong credit.
No tricks.
No hacks.
Just discipline.
And once your credit grows, so do your financial options.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to build credit in the US?
You can see a score within 1–3 months, but meaningful progress usually takes 6–12 months.
Is a secured credit card the best way to start?
For most beginners and immigrants, yes. It has the highest approval odds and builds history effectively.
Can I build credit without using the card?
No. You must use the card and allow activity to be reported.
Do I need to carry a balance?
No. Paying in full every month is ideal.
Conclusion
Starting from zero in a new country can feel overwhelming. But credit building in the US follows clear rules.
Understand them.
Follow them.
Be patient.
Within a year, you can move from “no credit” to a solid, growing financial profile.
And that is a powerful foundation for your life in America.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to build credit in the US?
Most people can see improvement in 3–6 months with consistent payments.
Can immigrants build credit in the US?
Yes, even without previous US credit history, you can start with secured cards.
What is the fastest way to build credit?
Pay on time, keep utilization low, and avoid opening too many accounts.
